| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | 31 |
- 월패드
- MQTT
- 공모주
- 파이썬
- 현대통신
- ConnectedHomeIP
- 국내주식
- Python
- 애플
- Apple
- Bestin
- esp32
- 티스토리챌린지
- 홈네트워크
- 매터
- raspberry pi
- 힐스테이트 광교산
- 오블완
- 해외주식
- 미국주식
- 코스피
- Home Assistant
- homebridge
- 배당
- matter
- Espressif
- 나스닥
- 마이크로소프트
- RS-485
- 라즈베리파이
- Today
- Total
YOGYUI
[ESP32] Pre-Provisioned Matter PAI, DAC 인증서 확인 본문

Parse pre-provisioned PAI, DAC certificates in secure_cert partition of ESP32
앞선 글에서 Matter pre-provisioned된 (EspressIf에서 제공하는 PAI, DAC 인증서가 포함된) ESP32의 secure_cert 파티션을 복호화한 뒤 텍스트 파일, 바이너리 파일로 저장하는 방법에 대해 알아봤다
[ESP32] Secure Cert 영역의 Pre-Provisioned 바이너리 추출해보기
[ESP32] Secure Cert 영역의 Pre-Provisioned 바이너리 추출해보기
Extract pre-provisioned binary from secure_cert partition of ESP32 ESP32를 이용한 Matter 제품 개발 시, 회사(혹은 개인) 차원의 PKI(Public Key Infrastructure, 공개 키 인프라)를 구축하지 않았다면 ESP32의 파티션 테이블
yogyui.tistory.com
이제 바이너리 파일을 파싱해서 내부에 들어있는 두 개의 인증서 정보를 가져오는 방법에 대해 알아보자
1. 사전 지식
esp-idf, esp-matter, connectedhomeip 등 matter 관련 소스코드를 열심히 파보며 알게된 사실들이다
- esp_secure_cert 파티션에 pre-provisioned되는 데이터는 TLV 형식이다
※ TLV: Title, Length, Value (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type%E2%80%93length%E2%80%93value) - X.509 공캐 키 인증서 2개가 들어있다 (Matter PAI, DAC)
- 내부에 포함될 수 있는 인증서 종류는 3가지가 있다
CA Cert(0), DAC (1), Private Key (2) - 인증서는 DER(Distinguished Encoding Rules) 포맷으로 인코딩되어 있다
2. X.509 DER 인증서 가져오기
- data[0:4]: 데이터의 최초 4바이트가 EspressIf에서 정한 TLV 매직바이트 0xBA5EBA11 인지를 확인한다
- data[4]: 플래그
- data[8:10]: 데이터 타입, 0 = CA Cert, 1 = DAC, 2 = Private Key
- data[10:12]: 데이터 길이 N
- data[12:12+N]: 원본 데이터
위의 파싱 규칙을 재귀호출하면 된다
원본 데이터는 python 설치 시 함께 설치되는 built-in 패키지인 cryptography의 X.509 모듈을 사용하면 된다
https://cryptography.io/en/latest/x509/reference/#x-509-certificate-object
X.509 Reference — Cryptography 43.0.0.dev1 documentation
CRL Entry Extensions These extensions are only valid within a RevokedCertificate object. class cryptography.x509.CertificateIssuer(general_names)[source] The certificate issuer is an extension that is only valid inside RevokedCertificate objects. If the in
cryptography.io
DER 인증서를 읽으려면 load_der_x509_certificate 함수를 호출하면 된다
다음과 같이 바이너리 파일을 파싱하는 코드를 손쉽게 구현할 수 있다 (python의 위대함!)
import os
from typing import List
from enum import IntEnum, auto
import cryptography.x509
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.serialization import Encoding
ESP_SECURE_CERT_TLV_MAGIC = bytearray([0xBA, 0x5E, 0xBA, 0x11])[::-1]
MIN_ALIGNMENT_REQUIRED = 16
class TLV_TYPE(IntEnum):
CA_CERT_TLV = 0,
DEV_CERT_TLV = auto()
PRIV_KEY_TLV = auto()
def parse_certificates(bin_file_path: str) -> List[cryptography.x509.Certificate]:
result = list()
with open(binpath, 'rb') as fp:
rawdata = bytearray(fp.read())
offset = 0
while True:
rawdata = rawdata[offset:]
tlv_header_magic = rawdata[:4]
if tlv_header_magic != ESP_SECURE_CERT_TLV_MAGIC:
break
print('Found TLV data')
tlv_header_flags = rawdata[4]
tlv_header_type = int.from_bytes(rawdata[8:10], signed=False, byteorder='little')
tlv_header_type = TLV_TYPE(tlv_header_type)
tlv_header_length = int.from_bytes(rawdata[10:12], byteorder='little')
padding_length = MIN_ALIGNMENT_REQUIRED - tlv_header_length % MIN_ALIGNMENT_REQUIRED
if padding_length == MIN_ALIGNMENT_REQUIRED:
padding_length = 0
crc_data_len = 12 + tlv_header_length + padding_length
print(f' tlv_header_flags: {tlv_header_flags}')
print(f' tlv_header_length: {tlv_header_length}')
print(f' tlv_header_type: {tlv_header_type.name}({tlv_header_type.value})')
# https://cryptography.io/en/latest/x509/reference/#x-509-certificate-object
cert_data = bytes(rawdata[12:12 + tlv_header_length])
certificate = cryptography.x509.load_der_x509_certificate(cert_data)
result.append(certificate)
offset += crc_data_len + 4
return result
추출한 바이너리 파일을 함수 인자에 넣어 호출하면 다음과 같은 출력을 확인할 수 있다
In [1]: certificates = parse_certificates('./esp_secure_cert.bin')
Out[1]:
Found TLV data
tlv_header_flags: 0
tlv_header_length: 555
tlv_header_type: DEV_CERT_TLV(1)
Found TLV data
tlv_header_flags: 0
tlv_header_length: 531
tlv_header_type: CA_CERT_TLV(0)3. 인증서 정보 확인
X.509 인증서 정보를 아래 함수로 간략하게 확인해보자
def print_certificate_info(cert: cryptography.x509.Certificate):
output_string = ''
output_string += f'cert version: {cert.version}\n'
output_string += f'cert serial number: {cert.serial_number}\n'
output_string += f'cert issuer: {cert.issuer}\n'
output_string += f'cert subject: {cert.subject}\n'
for attribute in cert.subject:
output_string += '\t' + str(attribute) + '\n'
output_string += f'cert not_valid_before: {cert.not_valid_before}\n'
output_string += f'cert not_valid_after: {cert.not_valid_after}\n'
output_string += f'cert signature_hash_algorithm: {cert.signature_hash_algorithm}\n'
output_string += f'cert signature_algorithm_oid: {cert.signature_algorithm_oid}\n'
output_string += 'cert extensions:\n'
for ext in cert.extensions:
output_string += '\t' + str(ext) + '\n'
# https://cryptography.io/en/latest/hazmat/primitives/asymmetric/ec/#cryptography.hazmat.primitives.asymmetric.ec.EllipticCurvePublicKey
# print(f'cert public key: {cert.public_key()}') # EllipticCurvePublicKey
output_string += 'cert public key:\n'
cert_pub_key_bytes = cert.public_bytes(encoding=Encoding.PEM)
output_string += cert_pub_key_bytes.decode(encoding='utf-8')
print(output_string)In [2]: print_certificate_info(certificates[0])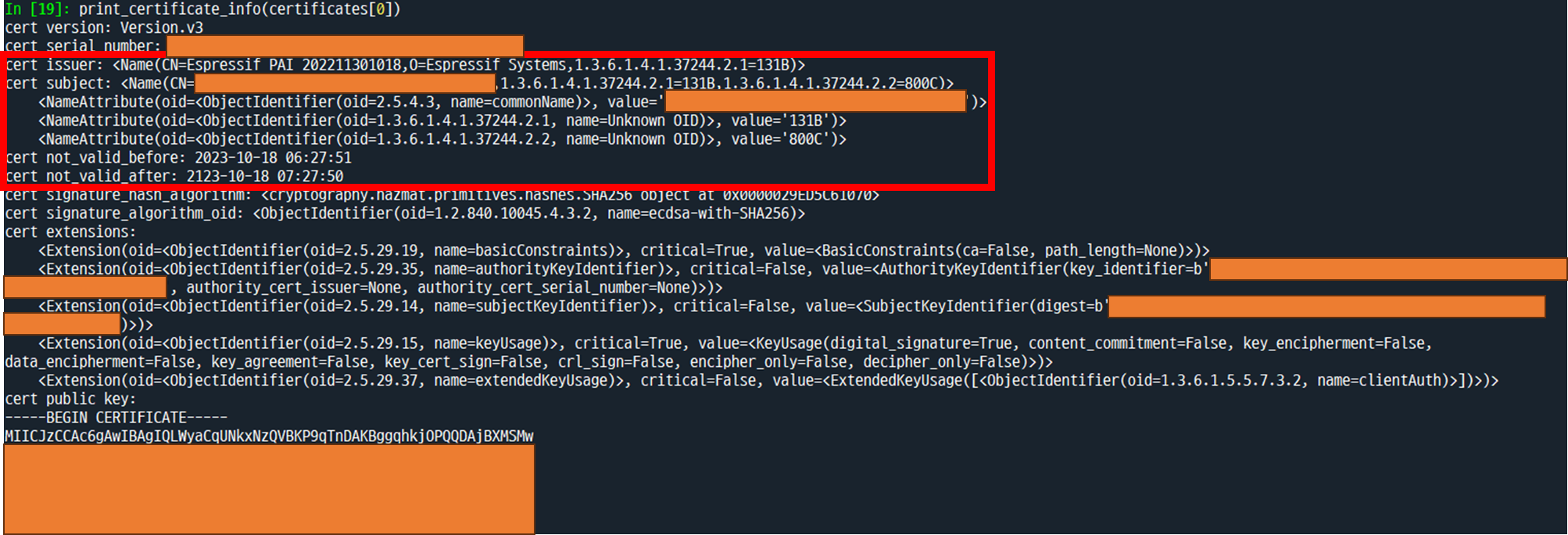
첫 번째 인증서는 DAC(Device Attestation Certificates) 인증서로, 발급자(issuer)가 EspressIf PAI 인 것을 알 수 있으며, 내부 정보로 Vendor ID 0x131B, Product ID 0x800C가 들어있는 것을 알 수 있다
※ EspressIf의 CSA 멤버십 Vendor ID가 0x131B 이다
그리고 인증서의 유효기간은 넉넉하게 100년 정도로 준 것을 확인할 수 있다
In [3]: print_certificate_info(certificates[1])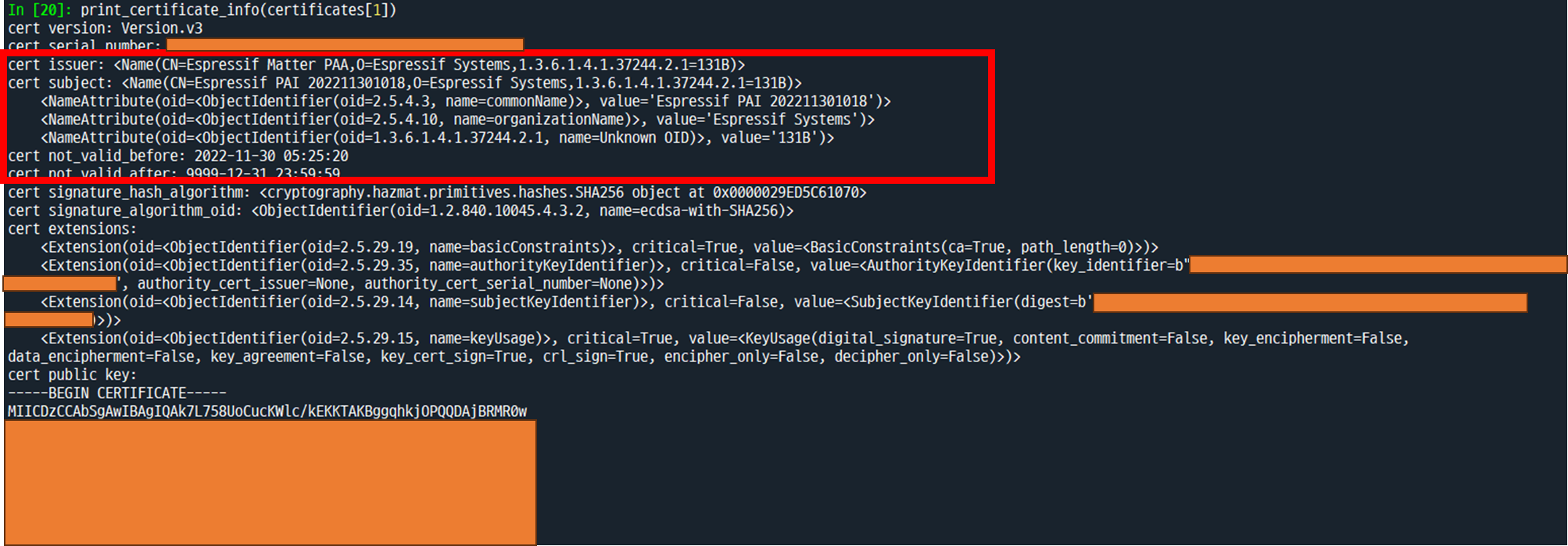
두 번째 인증서는 PAI(Product Attestation Authority)로, 위의 DAC 인증 시 사용된 인증서이며, 발급자는 EspressIf PAA인 것을 확인할 수 있다
4. 인증서 파일로 저장하기
DAC는 개별 제품마다 고유해야 하기 때문에 특정 장치에서 추출해낸 DAC를 딱히 어디 갖다 쓸 일은 없지만, 그래도 기념삼아 로컬에 파일로 저장해보자
def write_certificate_public_key(cert: cryptography.x509.Certificate, path: str):
cert_pub_key_bytes = cert.public_bytes(encoding=Encoding.PEM)
output_string = cert_pub_key_bytes.decode(encoding='utf-8')
with open(path, "w") as fp:
fp.write(output_string)In [4]: write_certificate_public_key(certificates[0], './matter_dac.pem')
In [5]: write_certificate_public_key(certificates[1], './matter_pai.pem')
끝~!
'홈네트워크(IoT) > Matter' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Matter Specification - Concentration Measurement Clusters (0) | 2024.02.13 |
|---|---|
| Matter Specification - Temperature Measurement Cluster (0) | 2024.02.13 |
| Matter - Test Harness User Manual 공식 문서 (from CSA) (0) | 2023.12.18 |
| Matter Specification - Fan Control Cluster (2) | 2023.11.19 |
| Matter Specification 1.2 발표 (23.10.23) (2) | 2023.10.24 |





